Plant embryology
Data: 1.09.2017 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 631Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Plant embryology
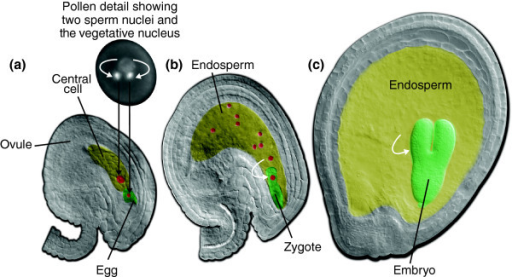
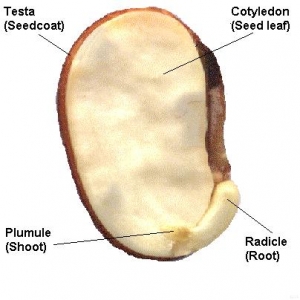
Looking for Embryology, Plant? Find out information about Embryology, Plant. the science of the origin and formation of new plants. View Plant Embryology presentations online, safely and virusfree! Learn new and interesting things. Get ideas for your own presentations. Plant embryology is one of the most important divisions of botany; its methods and goals are separate from those of plant morphology. General plant embryology explains the basic laws of the origin and development of generative and embryological structures (sporogenesis, gametogenesis, zygogenesis, endospermogenesis, embryogeny, apomixis). Embryo; Apomixis; Polyembryony; Seed; Embryology in relation to taxonomy; Experimental embryology; Palynology; Students can go to Amazon. com and find a nice collection of plant embryology textbooks. Additional selections of textbooks in this area can be found on Google. Part two deals with Plant Embryology and Palynology, and covers the structural life style, suitably divided into different chapters. Topics like Apomixis, Polyembryony, Experimental Embryology, Sexual Incompatibility, Classical and Applied Palynology, etc. , will certainly feature awareness in the subject. Plant development is an umbrella term for a broad spectrum of processes that include: the formation of a complete embryo from a zygote; seed. Plant embryology, or the development of a fullgrown plant from an embryo, contains some elements of development that is seen in different types of animals. There is an egg and a sperm which unite to form the fledgling zygote. Cambridge Core Cell Biology and Developmental Biology Molecular Embryology of Flowering Plants by Valayamghat Raghavan Please contribute to this project, if you have more information about this term feel free to edit this page. Drawing from a lifetime of teaching botany, Dr. Nels Lersten presents the study of the structures and processes involved in the reproduction of plants in his text. The development of the seed plant is basically different from that of an animal. The egg cell of a seed plant is retained within the enlarged lower part, or ovary, of. How can the answer be improved. Article on plant embryology by brayanseixas7840 Sharing Options. Share on Facebook, opens a new window; Share on Twitter, opens a new window Embryology (from Greek, embryon, the unborn, embryo; and, logia) is the branch of biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses. Additionally, embryology encompasses the study of congenital disorders that occur before birth, known as teratology. Buy Molecular Embryology of Flowering Plants on Amazon. com FREE SHIPPING on qualified orders In plants, the term embryogenesis covers development from the time of fertilization until dormancy occurs. The basic body plan of the sporophyte is established during. morphology: In biology, the study of the size, shape, and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms. Plant embryogenesis begins with an asymmetric cell division, resulting in a smaller apical (terminal) cell and a larger basal cell. This first asymmetric division provides polarity to the embryo. Most of the plant embryo develops from the apical (terminal) cell. The suspensor develops from the basal cell. The reproductive cycle of seed bearing plants has several stages. Plants flower, fruit, and produce new seeds. Inside each new seed there is a tiny plant embryo which. Define embryo: a vertebrate at any stage of development prior to birth or hatching embryo in a sentence
Related Images:
- 22 Holt Physics Study Guide Answers
- Charter Remote Guide Button Not Working
- Isi perjanjian aqabah pertama
- HP 2400 Scanjet Driver Windows 7zip
- C32 Marine Engine Rnc Cat
- Cracking decane gcse results
- Samsung C145 Mic Jumper Solution
- Estadisticas cancer de piel en chile
- Temple Oheb Shalom 1960 pdf
- Metodo Suzuki Para Flauta Dulce Pdf
- Libro Sociologia Anthony Giddens Quinta Edicion Pdf
- Gestire le risorse dellimpresapdf
- First Certificate Expert Coursebook
- The Signalman by Charles Dickenspdf
- Radiasi surya pdf
- Cars That Can Switch From Manuals To Automatic
- Fem Yaynlar Ygs Lys Kimya Konu Anlatml Pdf
- Casa dolce casapdf
- Legend of the Naga Pearls
- Kumpulan Puisi Pablo Nerudai1
- A Bad Case Of Tattle Tongue Lesson Plan
- Le repos du guerrier
- Venus Noire
- Serial Para Netsupport Manager 11
- Luther Vandross Greatest Hits
- PrinciplesOfMacroeconomicsExam1Answers
- Manual quality control 9 torrent
- Cca Exam Prep 2017
- Alter Ego 3 Guide Pedagogique Free Download
- Fac Wealth Techniques Collins Smith
- Kundalini Lenergia evolutiva delluomoepub
- Windows 7 all editions greek iso image
- Serial Number Asc Timetables
- Project Management and Human Resource Managmentpdf
- Forza Horizon 2 Xbox 360
- Roman Catholic Funeral Planning Guides
- Putra Salju
- The Book of Trees Visualizing Branches of Knowledge
- Yalom s cure dvd torrent
- Driver Graphtec Ce1000 60zip
- Ben 10 Alien Force Vilgax Attacks Psp Iso
- The Farmer Wants A Wife S09E01
- Download game gta for nokia asha 200
- 100 Years of Spanish Cinema
- Ati omega drivers 38330 download
- Micrografx picture publisher 10zip
- Ospedali salute Nono rapporto annuale 2011epub
- Farmacos antianginosos pdf
- Best Y Taylor Fisiologia 14 Edicion Pdf Descargar
- Download PDF EPUB Kindle Cardiff After Dark
- Clinical
- 50 Signs of the Times and the Second Coming
- Cheat Codepdf
- Tutorial Lightworks Bahasa Indonesiapdf
- Ingersoll Rand Air Compressors Customer Service
- Dieselfuelinjectorcleanercumminsfiltration
- Keyence Cv2100 User Manualpdf
- Sistemi energetici e macchine a fluido Vol 1pdf
- 2004 Chevrolet Silverado 2500hd Diesel Manuals
- Watch Online Foot Worship Sweaty Legs
- Economic Statecraft
- HLDTST DVDRAM GSA4167B SCSI CdRom Device driverzip
- First Dictionary
- In the Land of Blood and Honey
- Thailandpdf
- Edifice Efa 120d 7av Casio
- Is adam driver jewish
- Full Marks English Guide Class 7
- Manual De Microondas Mabe
- Price of a Kiss
- Whirlpool Akzm 794 Ix Manual
- Running Unblocked Games Weebly
- Chilton Repair Manuals For Motorcycles
- Software kode pos indonesia



.jpeg)